Configure ZTNA with on-premises resources and a Windows virtual machine
In this topic, you will learn how to configure the Portnox™ ZTNA remote private access method to allow your remote users to access your private resources hosted on-premises, by using a Docker container in an on-premises machine with Windows.
In this scenario:
-
You want your remote users to be able to access private web resources that you host on-premises.
-
You need to host a Portnox Docker container in the on-premises local network to be able to access these resources. You want to use a Windows-based virtual machine to run Docker Desktop and host the container.
We assume that you have already set up a physical or virtual machine on your chosen platform with Windows installed. We also assume that this machine is running in a network that has direct access to the resource.
We also assume that you already distributed certificates to your client devices.
Install Docker Desktop
In this section, you will learn how to follow Docker documentation to install Docker Desktop on the Windows machine.
Skip this section if Docker Desktop is already installed.
- Optional:
If you want to run Docker Desktop in a virtual machine, enable nested virtualization in your hypervisor on the host
machine.
This step depends on the hypervisor that you are using. Below are some examples for popular hypervisors. Consult the documentation of your hypervisor for more information.
-
Hyper-V: Execute the following command in PowerShell with administrative privileges:
Set-VMProcessor -VMName "vm_name" -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $truewhere vm_name is the name of your virtual machine.
-
VirtualBox: Go to and turn on the Enable Nested VT-x/AMD-V option.
-
VMware Workstation: Go to and turn on the Virtualize Intel VT-x/EPT or AMD-V/RVI option.
-
-
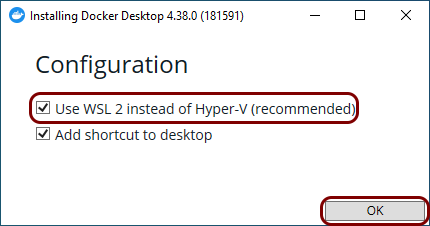
Enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) and install Ubuntu:
Note: For detailed instructions on how to enable WSL and install Ubuntu, see official Microsoft documentation.Note: You can run Docker Desktop with WSL or Hyper-V. WSL is recommended for performance reasons. If you need to run Docker Desktop with Hyper-V instead, refer to the official Docker and Microsoft documentation.
Result: WSL with Ubuntu is ready and you can proceed with Docker installation.
-
Install Docker Desktop:
Note: For detailed instructions on how to install Docker Desktop, see official Docker Desktop documentation.
-
Run Docker Desktop from the Start menu or the desktop icon.

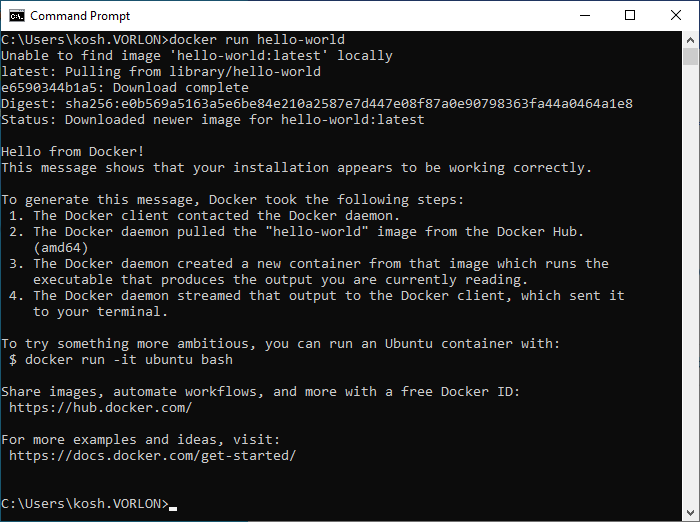
- Optional:
Test Docker in the Windows command line:
Set up the ZTNA gateway in Portnox Cloud
In this section, you will set up a ZTNA remote private access gateway in Portnox Cloud, install Docker on your machine, and run the Portnox ZTNA remote private access Docker container.
-
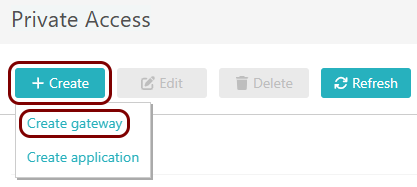
In the top menu of Portnox Cloud,
select the option. Then, on the Gateways screen, click on the + Create
gateway button.
-
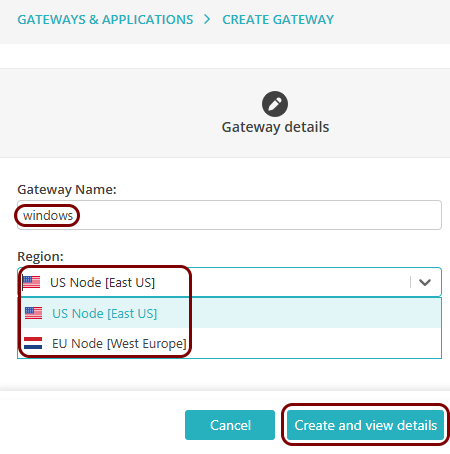
On the Create gateway screen, enter a name for this gateway in the
Gateway friendly name field, and in the Region field, select
either EUS Node 1, EUS Node 2, or WEU Node 1.
Then, click on the Create gateway and generate Docker commands button.
-
In the Provision container step, click on the Copy
command link under the displayed Docker command to copy the command to the clipboard.
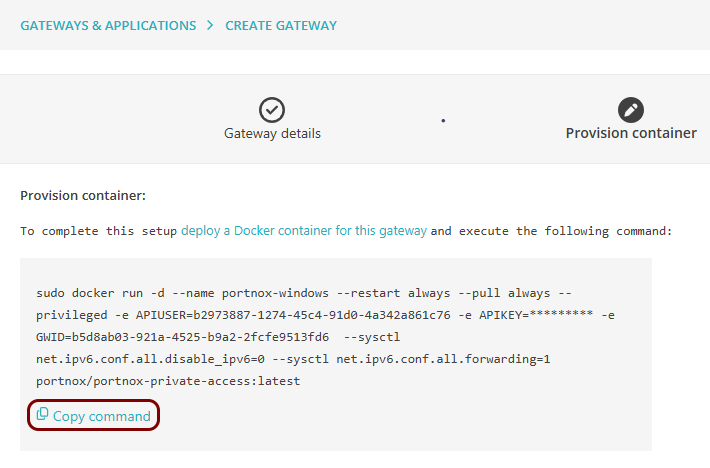
- Paste the command in a text editor and modify it for Windows (the original command is for Linux) by removing the sudo command at the start.
-
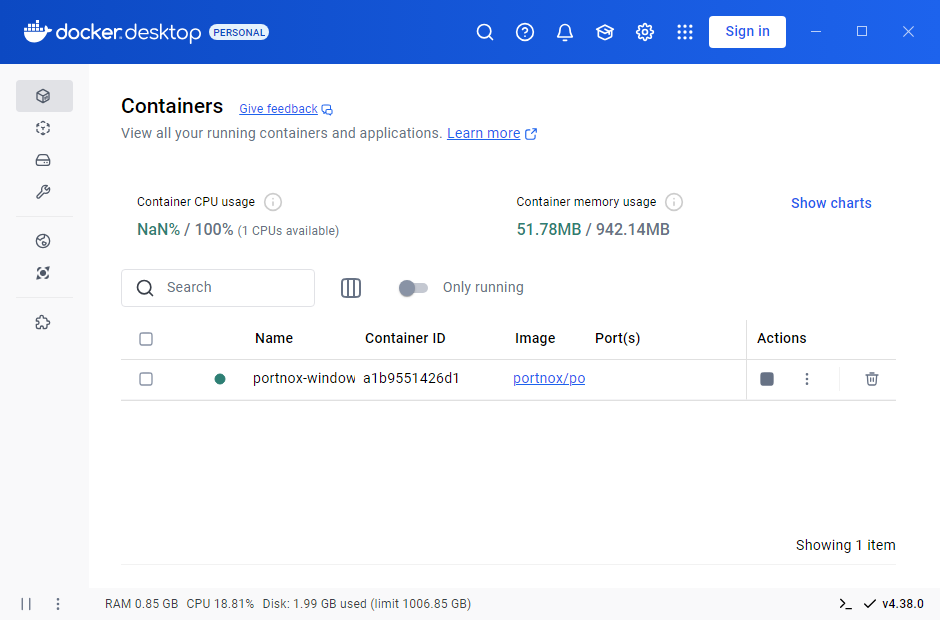
Paste the modified command in a command prompt window with administrative privileges to run the Docker
container.
Result: The Docker container is running in Docker Desktop.
Set up the ZTNA remote private access resource in Portnox Cloud
In this section, you will set up a ZTNA remote private access resource in Portnox Cloud and configure it to access your private resource hosted in the same local network as the Docker container.
-
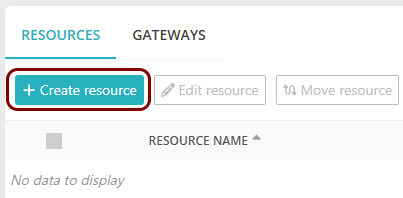
In the top menu of Portnox Cloud, select the option. Then, on the Resources screen, click on the + Create
resource button.
-
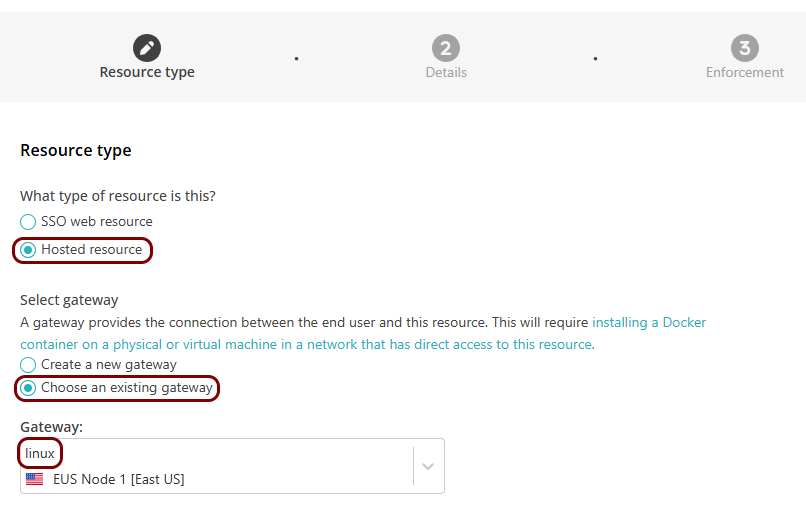
In the Resource type step, select the Hosted
resource option, and then the Choose an existing gateway option. In the
Gateway field, select the gateway that you have just created. Then, click on the
Next button.
-
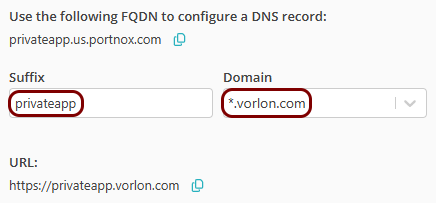
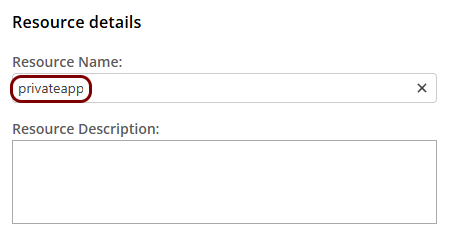
In the Details step, in the Resource Name field, enter the
name for this resource and optionally the Resource Description.
Note: The Resource Name must be a valid subdomain name, because the URL will be constructed using this name. You should only use lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens.
Result: If you want to use the Portnox URL, you can copy the URL for your resource by clicking on the ⧉ icon.
 Note: Make sure to check if your web resource will accept connections when accessed using this URL. If your web security solution has an anti-CSRF feature, you will need to configure it to allow this URL.
Note: Make sure to check if your web resource will accept connections when accessed using this URL. If your web security solution has an anti-CSRF feature, you will need to configure it to allow this URL. - Optional:
If your resource uses the same IP address and port as other resources:
Note: This is quite a common situation, for example, when you use a single on-premises web server to host several resources, and you create internal domain names for these resources such as: confluence.vorlon-onpremises.com or jira.vorlon-onpremises.com.
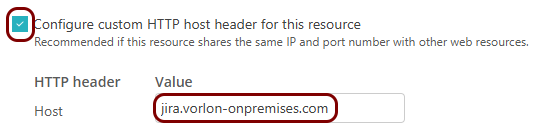
- Activate the Configure custom HTTP host header for this resource checkbox.
- In the Value column, enter the host header value.
- Optional:
If you want to use a URL in your own domain for the resource:
-
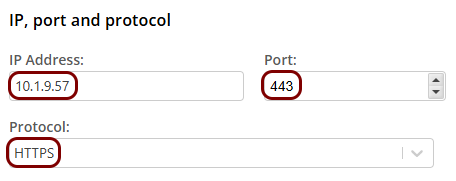
In the IP, port and protocol section, enter the details of the hosted resource in the
IP Address, Port, and Protocol
fields.
- Click on the Next button.
- Optional: In the Enforcement step, change the setting to Override with custom policy and then select a risk assessment policy if you want to control access to this resource using a custom risk assessment policy.
- Click on the Add resource button to save your configuration.
Result: Your users can now access your private resource by typing the URL in their browser.
Automatically update the existing local container
In this section, you will learn how to automatically update your Docker container to the latest version by deploying another Docker container: portnox-autoupdate.
-
Note down the organization ID:
-
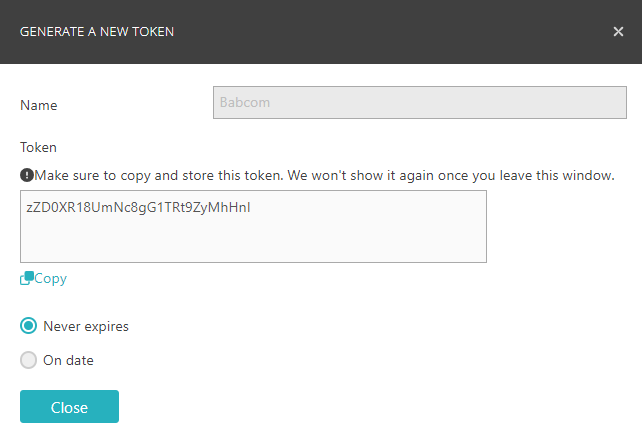
Get an API token from Portnox Cloud:
-
Deploy the portnox-autoupdate Docker container:
docker run --restart=always -d --name portnox-autoupdate ^ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock ^ -v portnox-autoupdate-logs:/app/logs ^ -e AUTO_UPDATE_ORG_ID=your_organization_ID ^ -e AUTO_UPDATE_PORTNOX_API_TOKEN=your_API_access_token ^ portnox/portnox-autoupdate:latestFor example:
docker run --restart=always -d --name portnox-autoupdate ^ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock ^ -v portnox-autoupdate-logs:/app/logs ^ -e AUTO_UPDATE_ORG_ID=b2973887-1274-45c4-91d0-4a342a861c76 ^ -e AUTO_UPDATE_PORTNOX_API_TOKEN=zZD0XR18UmNc8gG1TRt9ZyMhHnl ^ portnox/portnox-autoupdate:latest