Guest access – Fortinet
In this topic, you will learn how to configure Fortinet controllers to work together with the Portnox™ Cloud captive portal for guest user authentication.
Before you begin configuring your controller, you must do the following in Portnox Cloud:
-
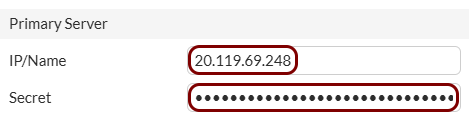
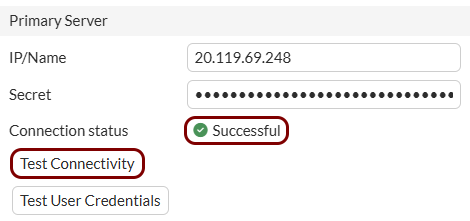
Open the Cloud RADIUS configuration, select your primary RADIUS instance, and copy the following values: Cloud RADIUS IP, Authentication port, and Shared Secret.
-
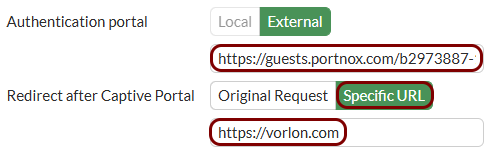
Configure the guest network in Portnox Cloud and note down the values of the fields: Captive Portal URL and IP (for walled garden).
Save these values in a temporary text file or keep your Portnox Cloud configuration open in another browser tab for easy copying and pasting.
Also, in the Fortinet web interface, make sure that your access points are authorized ().
You can create a captive portal configuration on Fortinet controllers in one of two modes: the local bridge mode or the tunnel mode. To create a captive portal configuration:
- First, follow the steps to create the RADIUS server (common for both modes)
- Then, optionally configure the TLS certificate (also common for both modes)
- Finally, select the mode that fits your network configuration.
In the local bridge mode, the controller is only responsible for configuration management. This mode is often used in teleworking, for example, if an employee uses a company access point at home. In the tunnel mode, all the traffic from the access point is tunnelled back to the controller.
Create the RADIUS server configuration
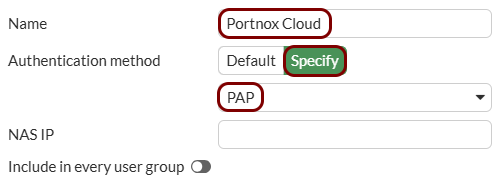
In this section, you will enter Portnox Cloud RADIUS server information in the Fortinet web interface and CLI.
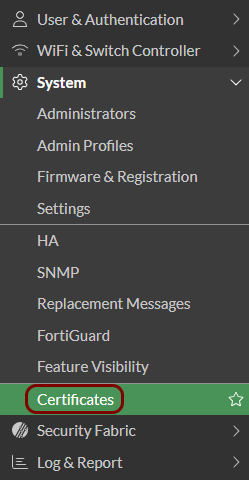
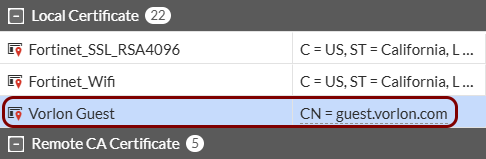
Configure the TLS certificate
Optional: In this section, you will upload and configure your own TLS certificate so you can use the captive portal in HTTPS mode.
If you do not complete these steps, most devices will display a warning that the captive portal is not working in a secure mode. If you want to avoid such warnings, and run the captive portal in secure mode (HTTPS):
- Obtain a domain or subdomain for your captive portal
- Configure that domain or subdomain in your DNS server
- Obtain a TLS certificate for that domain or subdomain.
To follow the steps below, you will need:
- The domain or subdomain name
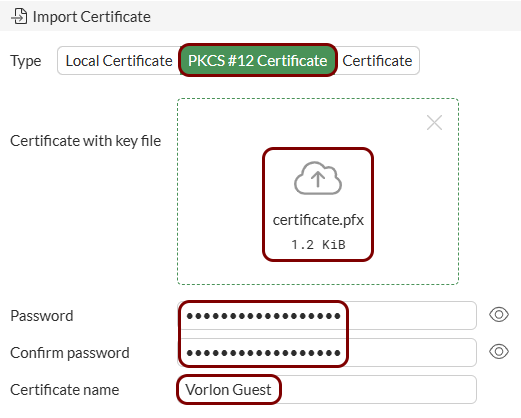
- The TLS certificate file for your domain or subdomain name together with the private key file (as a single PKCS#12 file or as two Base-64 encoded X.509 files)
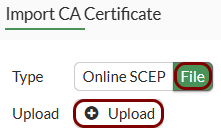
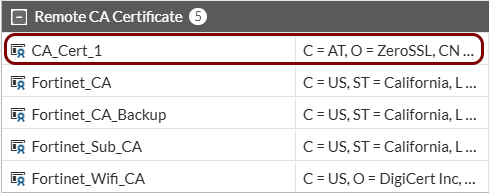
- The CA certificate file for the issuer of your TLS certificate in the Base-64 encoded X.509 format.
-
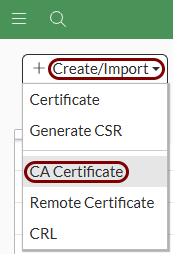
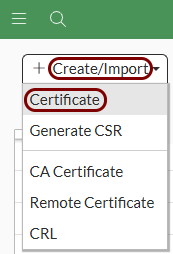
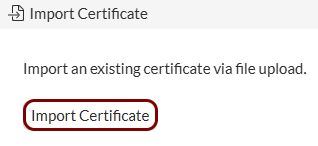
Import the certificates:
-
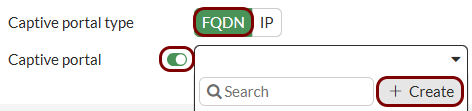
Configure authentication settings:
Set up the local bridge mode
In this section, you will set up a Portnox captive portal in a Fortinet controller using the local bridge mode.
Set up the tunnel mode
In this section, you will set up a Portnox captive portal in a Fortinet controller using the tunnel mode.
-
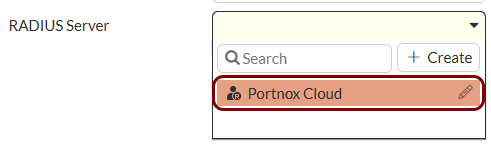
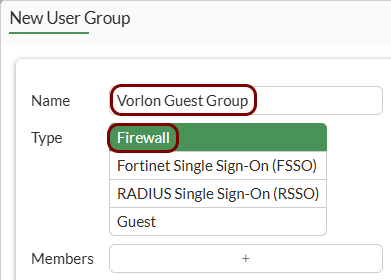
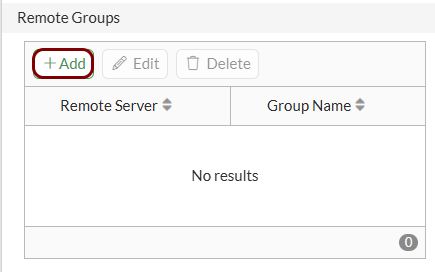
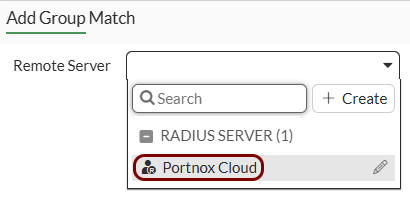
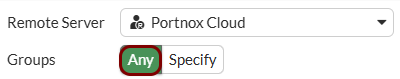
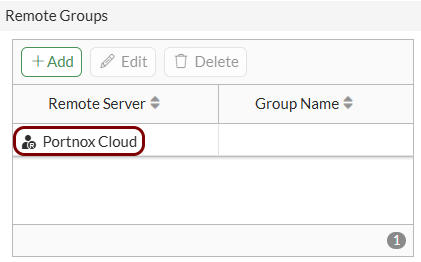
Create the user group for guest access:
-
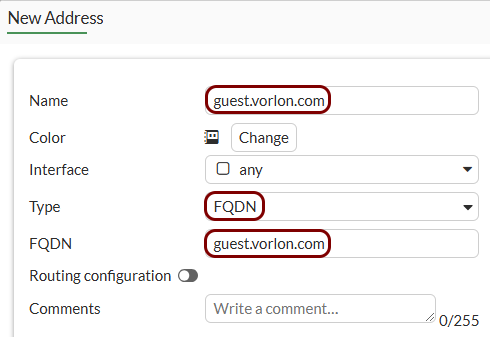
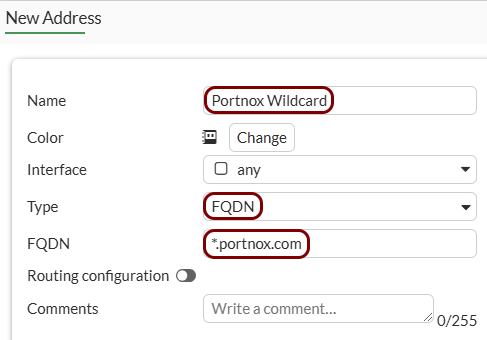
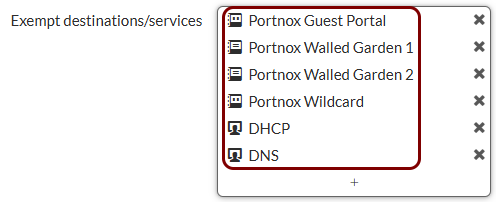
Create addresses for exemptions:
-
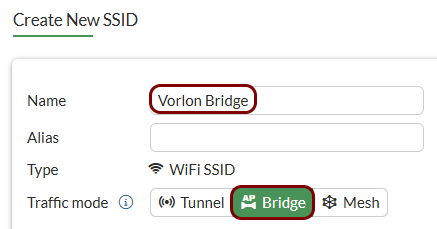
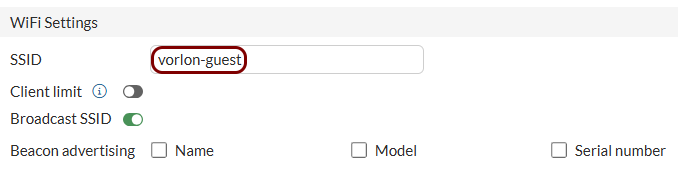
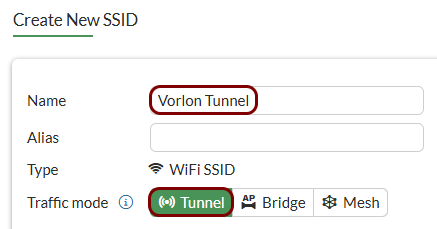
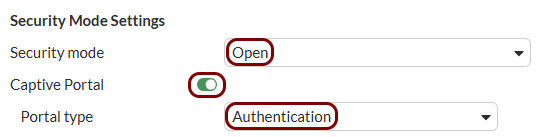
Create an SSID for the captive portal:
-
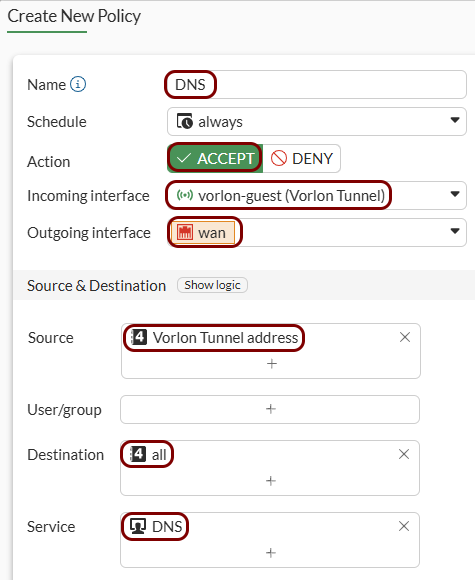
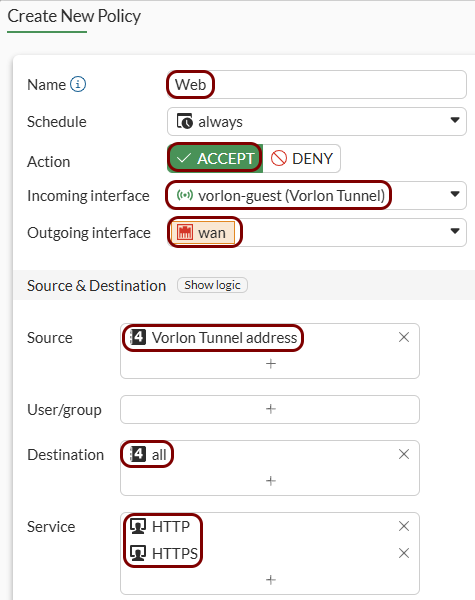
Create security policy rules:
-
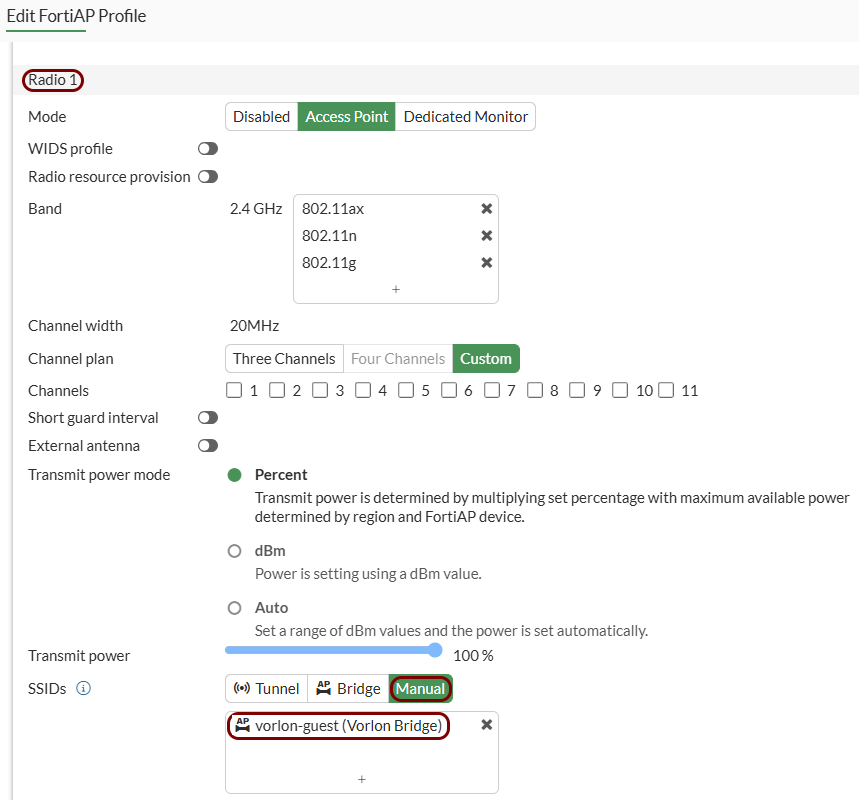
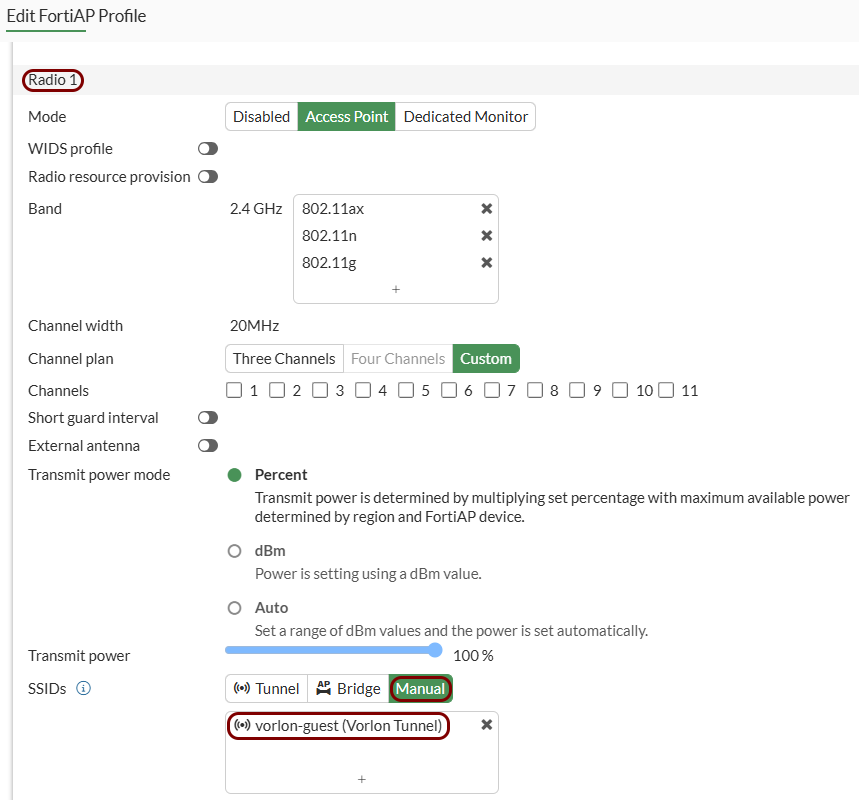
Add the new guest SSID to your access point: