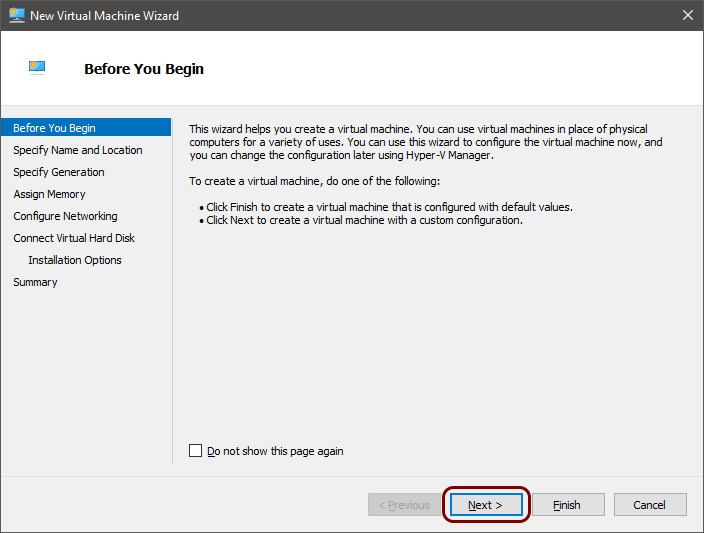
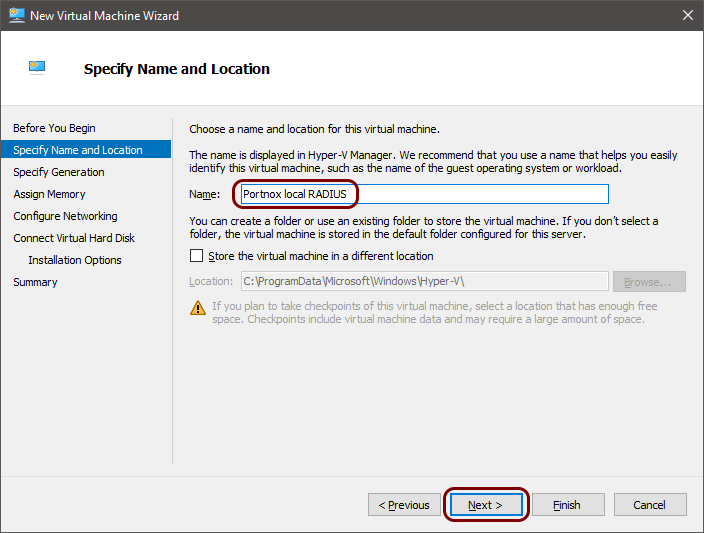
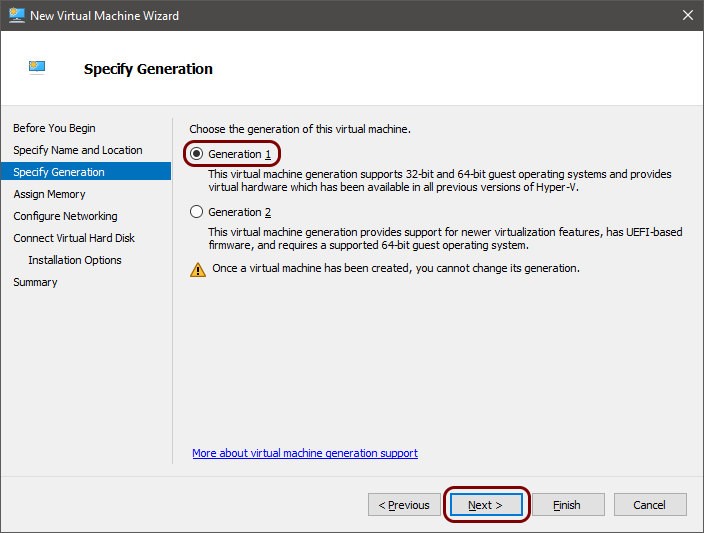
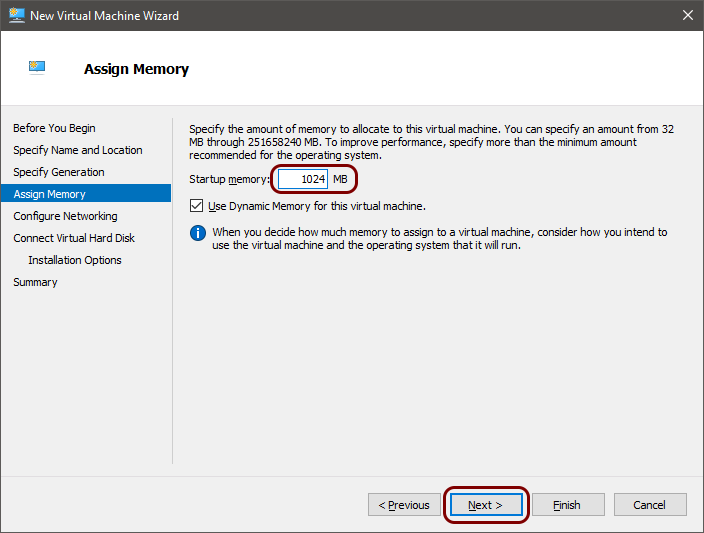
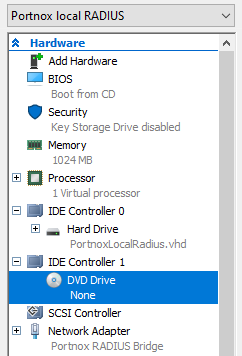
Run the local RADIUS server in Microsoft Hyper-V
In this topic, you will learn how to install and configure the Portnox™ Cloud local RADIUS proxy in the Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor.
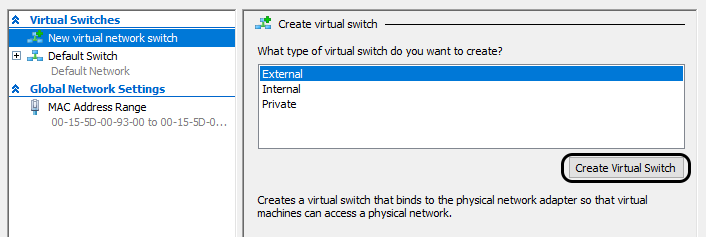
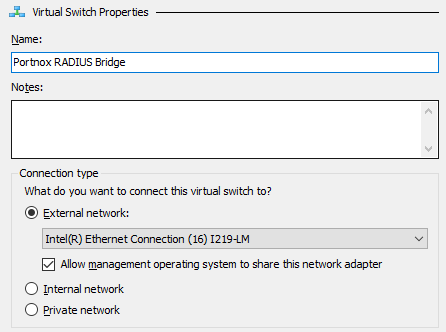
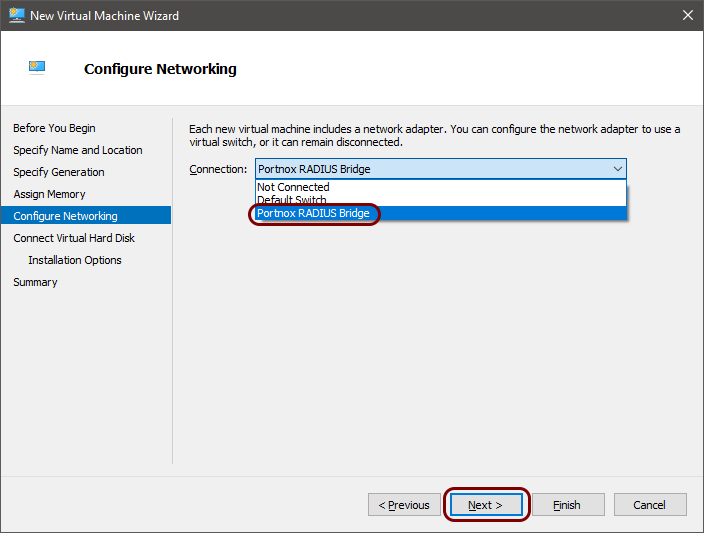
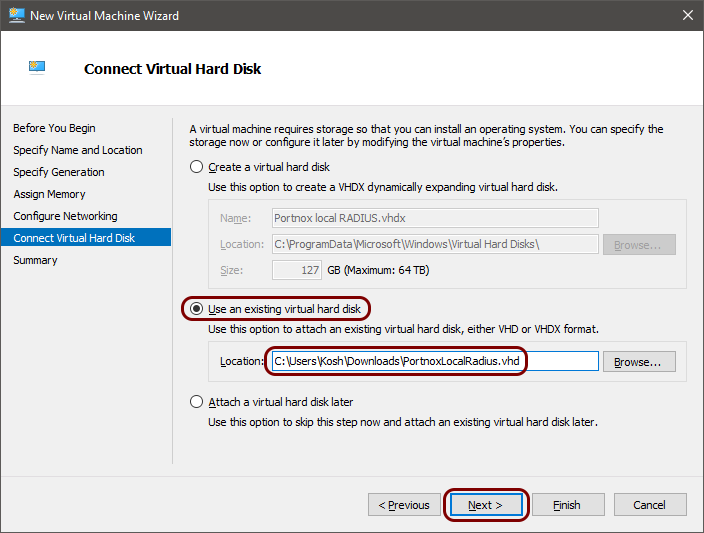
To configure the local RADIUS proxy in the Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor, you must first:
- Download the local RADIUS server virtual machine file for Hyper-V, VHD format
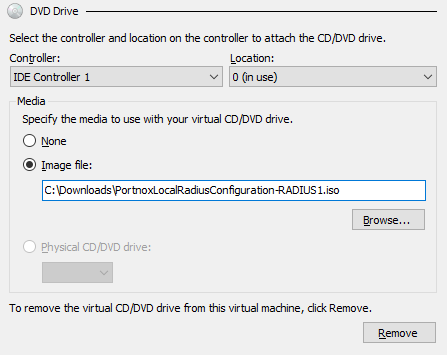
- Configure the settings for the local RADIUS server and download the configuration for the virtual machine file.
To do these steps, go to the following topic: Set up a local RADIUS server using a virtual machine.
Warning:
The performance of a local RADIUS server depends on how many RADIUS authentication and
accounting packets it processes, which cannot be predicted in advance. At a minimum, a local RADIUS server needs 1 CPU and 4
GB of RAM. This is enough for most customers, but actual results may vary. Customers should monitor the server’s performance and add more resources if needed to
avoid overloading it. For very large setups, it’s recommended to use up to 8 CPUs with a combined PassMark score above
14,000, 32 GB of RAM, and SSD storage. This setup is similar to a higher-end laptop.
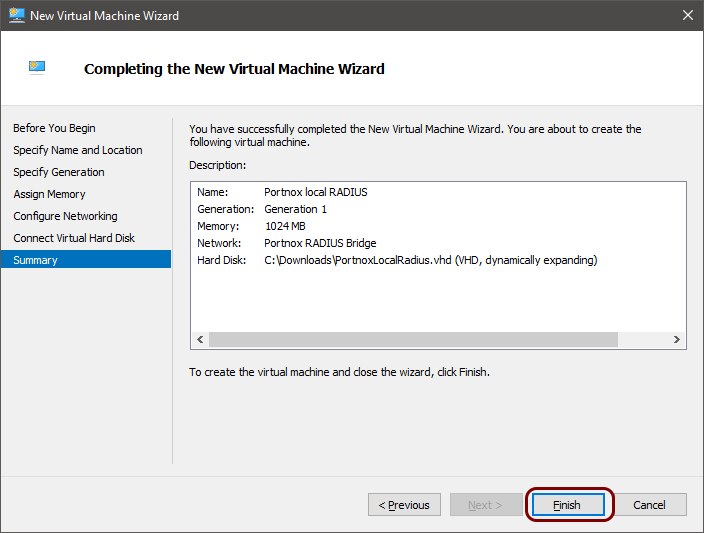
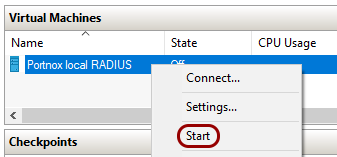
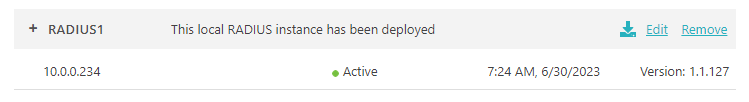
Result: Your local RADIUS server is active.
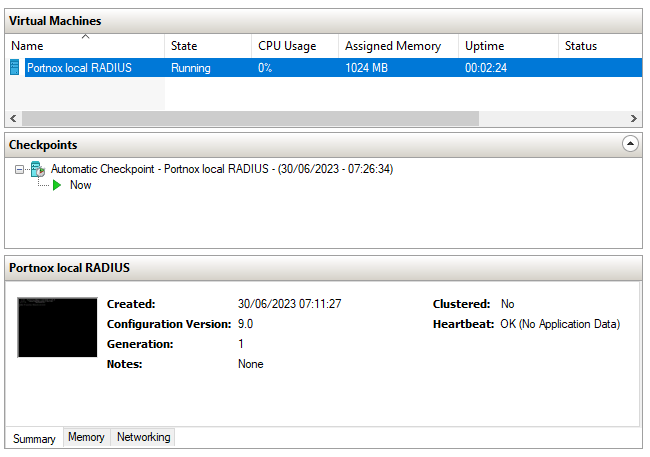
You can check its status in Portnox Cloud, in the section.
Note:
If you have connectivity issues with your local RADIUS server, check the following topic: How to set up the firewall for the local RADIUS instance to connect to Portnox Cloud.